
If, however, the actual rate of pay per hour is greater than the standard rate of pay per hour, the variance will be unfavorable. If the exam takes longer than expected, the doctor is not compensated for that extra time. Doctors know the standard and try to schedule accordingly so a variance does not exist. If anything, they try to produce a favorable variance by seeing more patients in a quicker time frame to maximize their compensation potential. If the outcome is unfavorable, the actual costs related to labor were more than the expected (standard) costs. If the outcome is favorable, the actual costs related to labor are less than the expected (standard) costs.
About Dummies
All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Direct Labor Mix Variance shows how much production is wasted and can be used as a tool to decrease Direct Labor Mix Variance.
Best Practices for Managing Labor Variances
The goal is to identify discrepancies that indicate either over- or under-utilization of labor resources or deviations in labor costs. The direct labor variance measures how efficiently the company uses labor as well as how effective it is at pricing labor. There are two components to a labor variance, the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor time variance.
Definition of Labor Rate Variance
- The following equations summarize the calculations for direct labor cost variance.
- By understanding the causes of labor variances and implementing targeted corrective actions, companies can enhance labor cost control, improve efficiency, and boost overall productivity.
- To compute the direct labor quantity variance, subtract the standard cost of direct labor ($48,000) from the actual hours of direct labor at standard rate ($43,200).
- Calculating DLYV can help organizations better control their labor costs, optimize production processes, and improve overall profitability.
- With either of these formulas, the actual hours worked refers to the actual number of hours used at the actual production output.
Another important reason of an unfavorable labor efficiency variance may be insufficient demand for company’s products. Outcome By addressing these issues, Company A was able to reduce its unfavorable labor rate variance significantly in subsequent quarters, achieving better cost control and financial stability. The quality of training and supervision significantly affects labor efficiency. Well-trained workers and effective supervision can enhance productivity, leading to favorable labor efficiency variances. Inadequate training or poor supervision can result in inefficiencies and unfavorable variances. To put it simply, if your workers are taking longer to complete a task, your labor costs will go up.
Regular variance analysis helps management identify areas where labor costs deviate from the budget, enabling them to take corrective actions promptly. This analysis supports better decision-making, enhances financial performance, and ensures resources are used optimally. This results in an unfavorable labor rate variance of $2,000, indicating that the company spent $2,000 more on labor than anticipated due to higher wage rates. Changes in the labor market, such as a shortage of skilled workers or new labor agreements, can lead to wage adjustments. These changes may cause the actual hourly rate to deviate from the standard rate, resulting in a labor rate variance.
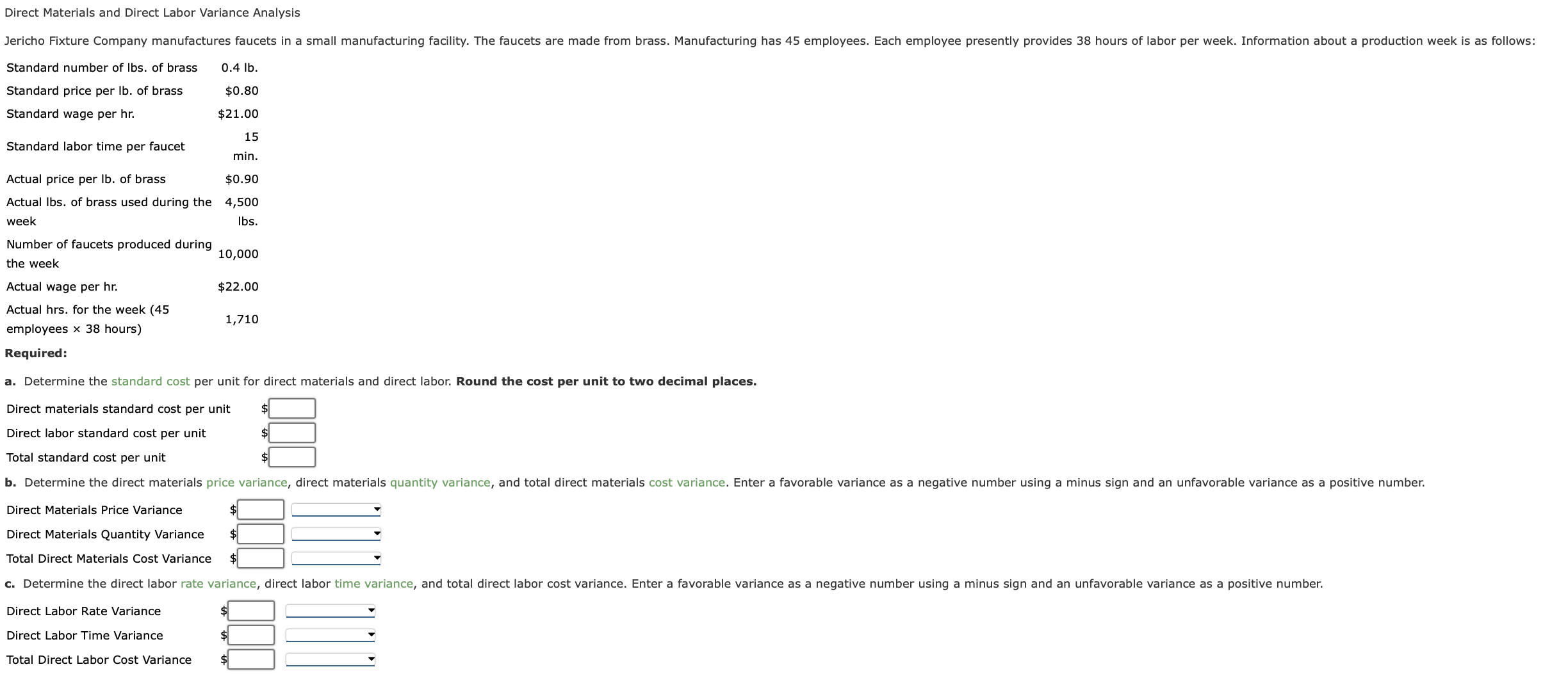
Labor rate variance is the total difference between the total paid amount for a certain amount of labor and the standard amount that the labor usually commands. Managers can better address this situation if they have a breakdown of the variances between quantity and rate. To estimate how the combination of wages and hours affects total costs, compute the total direct labor variance. As with direct materials, the price and quantity variances add up to the total direct labor variance. Calculate the labor rate variance, labor time variance, and total labor variance. Skill workers with high hourly rates of pay may be given duties that require little skill and call for low hourly rates of pay.
Labor rate variance is a measure used in cost accounting to evaluate the difference between the actual hourly wage rate paid to workers and the standard hourly wage rate that was anticipated or budgeted. This variance highlights whether the company is paying more or less for labor than expected, providing insights into the efficiency of labor cost management. Understanding labor rate variance helps companies manage labor costs more effectively by identifying discrepancies between automatic extension actual and standard wage rates. By analyzing these variances, businesses can take corrective actions to align their labor expenses with budgeted costs, ultimately improving financial performance and cost control. The direct labor efficiency variance may be computed either in hours or in dollars. Suppose, for example, the standard time to manufacture a product is one hour but the product is completed in 1.15 hours, the variance in hours would be 0.15 hours – unfavorable.
This will result in an unfavorable labor rate variance, since the actual hourly rate of pay will exceed the standard rate specified for the particular task. In contrast, a favorable rate variance would result when workers who are paid at a rate lower than specified in the standard are assigned to the task. Finally, overtime work at premium rates can be reason of an unfavorable labor price variance if the overtime premium is charged to the labor account. Direct labor variance is calculated by comparing the actual hours worked and the actual hourly wage rate against the standard hours allowed for the actual production level and the standard wage rate.
