
Moreover, although typically a higher accounts receivable turnover ratio is preferable, there are also scenarios in which your ratio could be too high. A too high ratio can mean that your credit policies are too aggressive, which what are dilutive securities dilutive securities meaning and definition can lead to upset customers or a missed sales opportunity from a customer with slightly lower credit. Essentially, it gives insight into the efficiency of a company’s credit policies and accounts receivable management.
What is Accounts Receivable (AR) Turnover Ratio?
An accounts receivable is the sum of the beginning and ending account balances divided by two. The year-over-year growth formula is one of the most reliable ways of tracking your long-term growth. Picking the right fiscal year for your business can save you and your accountant a lot of time, money and stress. Our intuitive software automates the busywork with powerful tools and features designed to help you simplify your financial management and make informed business decisions. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.
Suze Orman: This Is the First Bill You Need To Pay Each Month
- Using the accounts receivable turnover calculator is one thing and understanding the data coming out of it is completely another ball game altogether.
- Companies are more liquid the faster they can covert their receivables into cash.
- In a sense, this is a rough calculation of the average receivables for the year.
- Here are some examples in which an average collection period can affect a business in a positive or negative way.
- A consistently low ratio indicates a company’s invoice terms are too long.
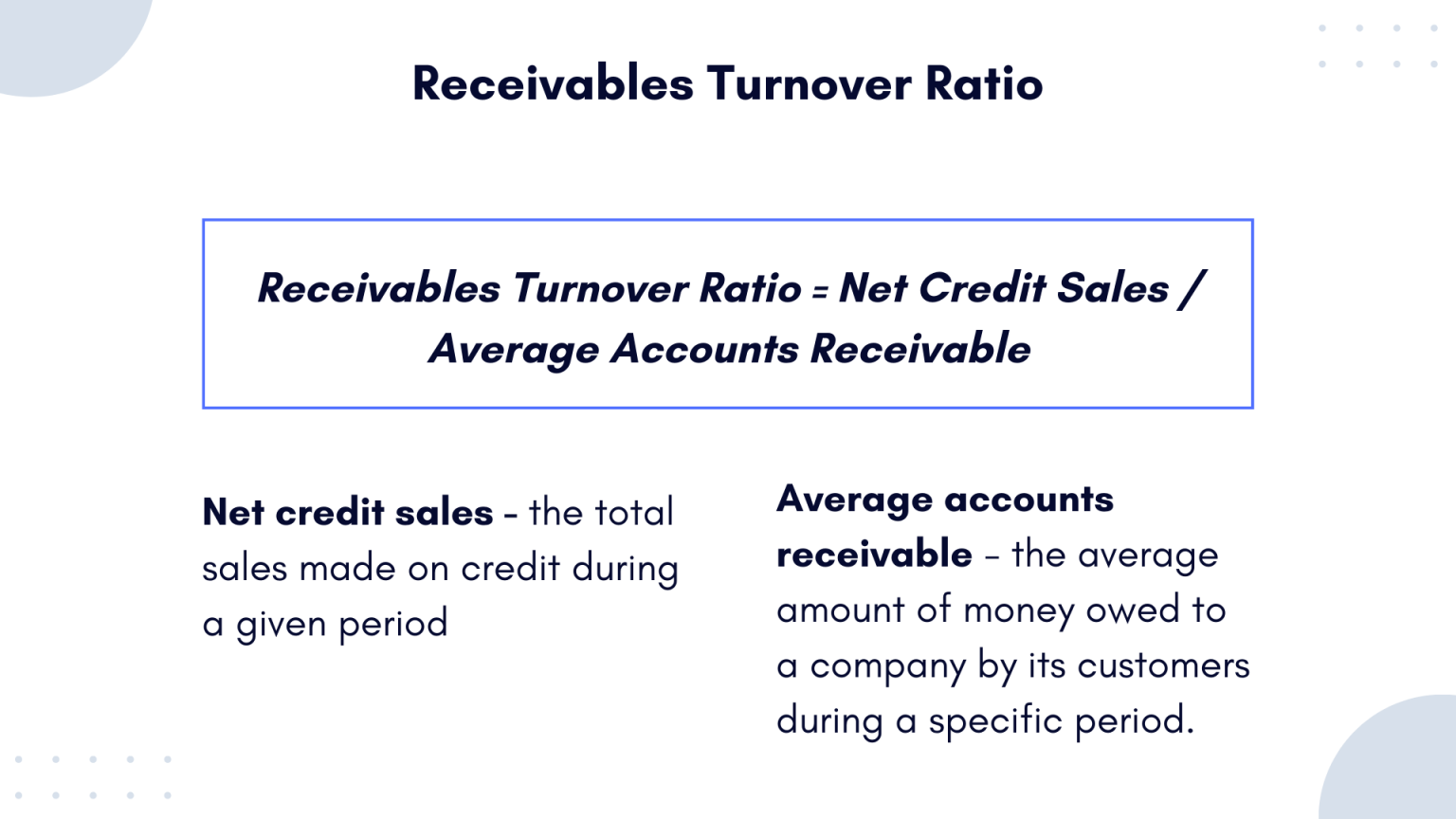
You’ll divide your net credit sales by your average accounts receivable to calculate your accounts receivable turnover ratio, or rate. The accounts receivable turnover ratio is comprised of net credit sales and accounts receivable. A company can improve its ratio calculation by being more conscious of who it offers credit sales to in addition to deploying internal resources towards the collection of outstanding debts.
Accounting Services
Ensure to follow up with your customers and still grant some flexibility if needed, like payment options or payment plans, for your customers. AR turnover ratio and AP turnover ratio are both important but focus on difference aspects of financial health, just like how AR and AP themselves are different. A high ratio would be around 7 to 8, but what is considered a high ratio is also dependent on the industry you are in. The portion of A/R determined to no longer be collectible – i.e. “bad debt” – is left unfulfilled and is a monetary loss incurred by the company.
Incentivize cash sales
Although this metric is not perfect, it’s a useful way to assess the strength of your credit policy and your efficiency when it comes to accounts receivables. Plus, if you discover that your ratio is particularly high or low, you can work on adjusting your policies and processes to improve the overall health and growth of your business. Companies can optimize their collection efforts by adopting a proactive approach towards outstanding invoices. They should consider segmenting their customer base according to creditworthiness and invoice due dates, prioritizing collections from customers who consistently pay late. Regularly reviewing the accounts receivable aging report aids in identifying overdue payments and allows them to act swiftly. Calculating the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio is crucial for measuring a company’s efficiency in collecting credit sales.
A high receivables turnover ratio might also indicate that a company operates on a cash basis. The asset turnover ratio is a valuable financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in using its assets to generate revenue. By understanding this ratio, you can gain insights into a company’s effectiveness in using its assets to drive sales. By accepting insurance payments and cash payments from patients, a local doctor’s office has a mixture of credit and cash sales.
However, if a company with a low ratio improves its collection process, it might lead to an influx of cash from collecting on old credit or receivables. An unusually high accounts receivable balance relative to revenue may suggest poor collection practices or relaxed credit policies. If Company E has accounts receivable totaling 400,000 dollars against annual revenue of 1 million dollar, this 40% ratio could indicate slower collections, which may impact cash flow. Similarly, if inventory levels are rising faster than sales, there may be an excess inventory issue, leading to potential obsolescence or discounting.
Conversely, a low ratio may signal inefficiencies or the need for strategic changes. However, it’s important to consider industry norms when evaluating this ratio, as asset utilization varies significantly across sectors. For example, a company that invests in technology or AI may find that they can streamline production to improve asset turnover. In contrast, a company that overinvests in underperforming assets will see how it adversely impacts the asset turnover ratio.
It is much like the inventory turnover ratio which measures how fast the inventory is moving in a business. Maria’s receivables turnover ratio is 6 times for the year 2023 which means it, on average, has collected its receivables 6 times during the year. To analyze how efficient the company has been in collecting its receivables during this period, it can compare this ratio with its competing entities as well as the past years’ ratio of its own.
